# Java多线程
# 创建线程三种方式
- 继承Thread类,重写run方法
class Thread1 extends Thread { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("当前线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } //测试 Thread t1 = new Thread1(); t1.setName("t1"); t1.start();1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 - 实现Runable接口,实现run方法
class Thread2 implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { System.out.println("当前线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } } //测试 Thread2 t2 = new Thread2(); new Thread(t2 , "t2").start();1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 - 实现Callable接口,重写call()方法。有返回值
class Thread3 implements Callable<String> { @Override public String call() throws Exception { System.out.println("当前线程" + Thread.currentThread().getName()); return "ok"; } } //测试 Thread3 t3 = new Thread3(); FutureTask<String> ft3 = new FutureTask<>(t3); new Thread(ft3).start(); System.out.println(ft3.get());1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
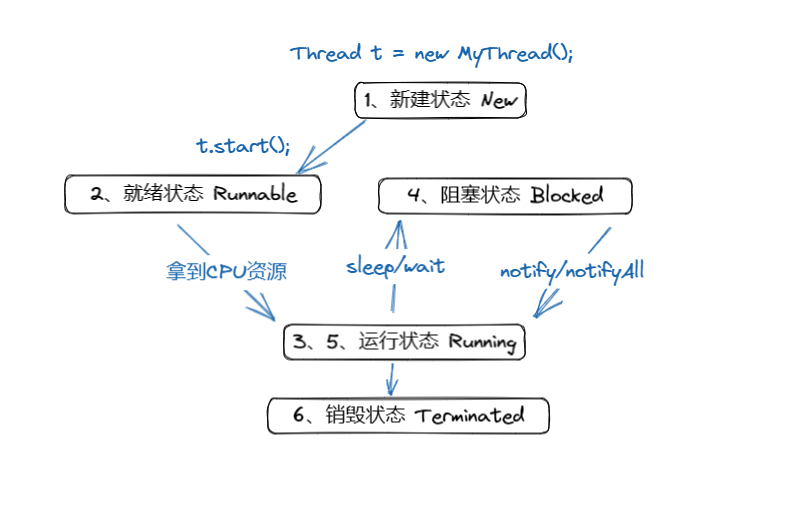
# 线程的周期